Case-Mix Systems
Case-mix systems classify individuals into case-mix groups based on similar resource utilization and care needs. Using this system promotes systematic distribution of resources by aligning funding with the intensity of support a participant requires.
- Case-mix groups are designed specifically to improve resource allocation and service planning for individuals in different populations.
- Developed using the various interRAI assessment forms to inform algorithm triggers and linked assessment records with paid claims to guide development.
- Case-mix groups have high predictive validity and effectively distinguish between individuals with varying support needs.
- Case-mix groups align with the interRAI's assessment framework, using standardized and validated data to determine care intensity. These vary depending on the interRAI assessment in use.
Case-Mix Index
Case-mix groups are utilized to identify the participant's case mix index (CMI). The CMI indicates the cost to serve a participant relative to the average cost to serve. The CMI is a standardized output that is available for each participant for certain versions of the interRAI.
- The average cost to serve a participant is represented by a CMI of 1.0.
- A CMI of less than 1.0 costs less than average to serve.
- A CMI greater than 1.0 costs more than average to serve.
- A CMI of 2 would indicate it costs 200% of the average cost to serve.
Alignment to Nebraska's Funding Tiers
Nebraska's Comprehensive Developmental Disabilities (CDD) and Developmental Disabilities Adult Day (DDAD) waivers offer a five-tier budget system; Basic, Intermediate, High, Advanced, and Risk Tier.
Risk Tier recommendations are made through an exception process and are highly variable depending on a participant's needs. The CMI is not being utilized to determine Risk Tier budget amounts. CMI scores were aligned to the other four tiers of Nebraska's existing budget system.
Case-Mix Index Ranges and Nebraska's Funding Tiers
The children and youth budget system utilizes the Child and Youth Resource Index (ChYRI) groupings. [1] The adult budget system utilizes the Case-Mix Groups for Developmental Disability (CMGDD) groupings. [2] Participants of all ages utilize the same CMI range for funding tier alignment.
Nebraska Funding Tier CMI Alignment
| Nebraska Funding Tier | Child/Youth ChYRI Groups | Adult Group Number | CMI Range |
| Basic | E | 1 to 4 | .45 to .75 |
| Intermediate | G, F | 5 to 20 | .76 to 1.23 |
| High | D, H, A | 21 to 29 | 1.24 to 1.5 |
| Advanced | B, C
| 30 to 33
| 1.51 to 2.01
|
DD Waiver Populations by TierThe graphs below display DD Waiver populations in different months, beginning in January 2025.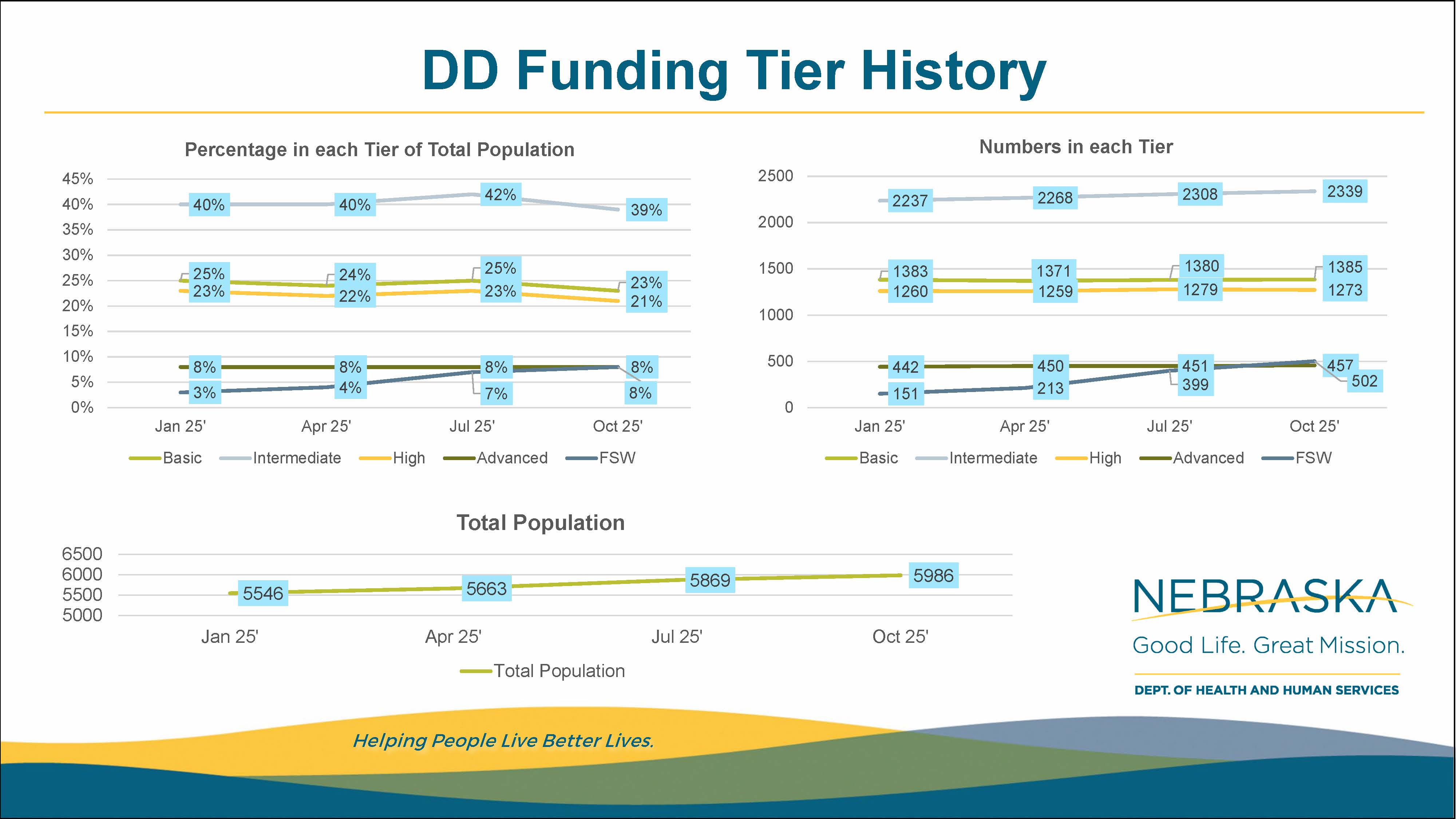 View PDF of Funding Tier History
View PDF of Funding Tier History[1] Stewart et al. A Case-Mix System for Children and Youth with Developmental Disabilities. (July 2020). Accessed 12, November 2025.
[2] Fries et al. A Case-Mix System for Adults with Developmental Disabilities. (May 2019). Accessed 12, November 2025.